Examples
Coarse-graining water molecules
We derive coarse-grained water-water non-bonded effective potentials such that the structural properties of the underlying atomistic system are reproduced. The coarse-grained model is set up by mapping a water molecule to a one-bead representation located at the center of mass of molecule.
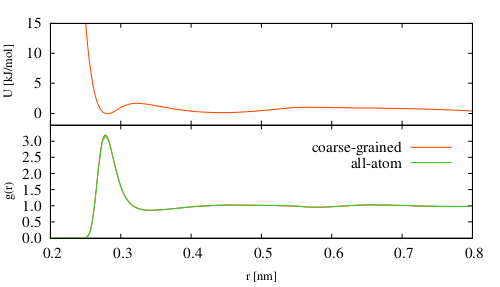
Atomistic simulation was used to calculate the radial distribution function (RDF) between centers of mass of water molecules. The simulation box contained 510 TIP3P water molecules (1530 atoms), with a side length of 2.5 nm. Standard periodic boundary conditions and the minimum image convention were used. Temperature was regulated at 300 K using a local Langevin thermostat with the value of friction constant 5 ps-1.
At the below link is located a project with these files. Atomistic RDF (water-water) is loaded as the target distribution. The distribution files are already smoothed. For clarity, the obtained distribution and potential files are provided for every fifth iteration only (from 29 iterations).
Coarse-graining a salt solution
In this example we derive effective potentials for a NaCl salt solution, i.e.. between water-water, water-Cl and water-Na. The coarse-grained model is set up by mapping a water molecule to a one-bead representation located at the center of mass of molecule.
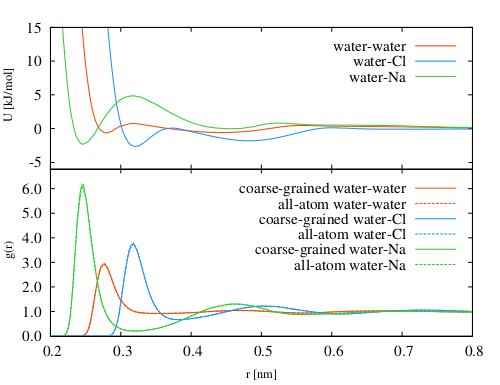
Atomistic simulation was run to obtain reference radial distribution functions. We used a standard SPC/E water model with AMBER forcefield for ions. Generalized reaction field method was used for electrostatic interactions with cutoff radius Rc = 0.9 nm, epsilon1 = 1, epsilon2 = 80, and the Debye screening length κ = 3.25 nm-1. Integration was done with standard velocity Verlet with a time-step of 1 fs. Langevin thermostat with the friction constant 15 ps-1 was used to regulate temperature at 300 K. Size of the system was 16.08 x 4.02 x 4.02 nm3, containing 8377 water molecules and 157 Na and 157 Cl ions, corresponding to a 1 M salt solution. Geometry of water molecules was constrained with SETTLE algorithm.
At the below link is located a project with these files. Atomistic RDFs (water-water, water-cl, water-na) are loaded as the target distributions. The distribution files are already smoothed. For clarity, the obtained distribution and potential files are provided for 0th, 10th and last iteration only (from 17 iterations).